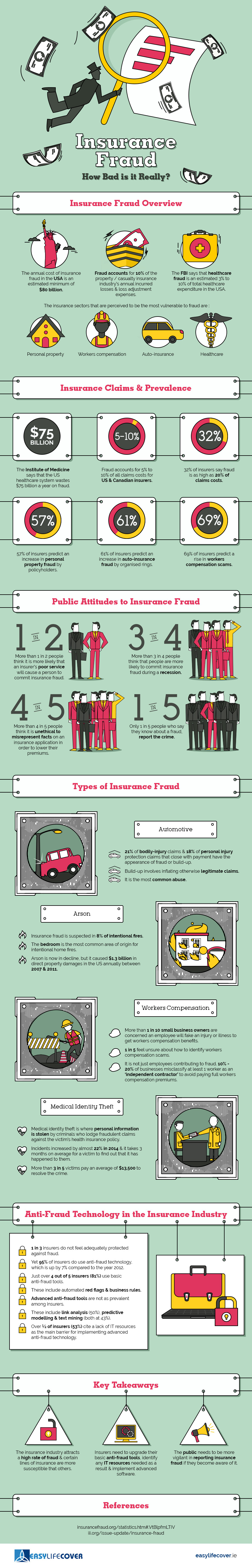
Did you know that the annual cost of insurance fraud in the United States is an estimated minimum of 80 billion! In fact, fraud accounts for 10% of the property / casualty insurance industry’s annual incurred losses and loss adjustment expenses. Additionally, the FBI says that healthcare fraud is an estimated 3% to 10% of total healthcare expenditure in the U.S.
In the following infographic, learn more about how bad and widespread insurance fraud really is. If you suspect insurance fraud and are in need of a professional insurance fraud investigator, be sure to contact us.
[Click image for full size version]
Insurance Fraud: How Bad is it Really?
Insurance Fraud Overview
- The annual cost of Insurance fraud in the USA is an estimated minimum of $80 billion.
- Fraud accounts for 10% of the property / casualty insurance industry’s annual incurred losses and loss adjustment expenses.
- The FBI says that healthcare fraud is an estimated 3% to 10% of total healthcare expenditure in the USA.
The insurance sectors that are perceived to be the most vulnerable to fraud are:
- Personal Property
- Workers Compensation
- Auto-Insurance
- Healthcare
Insurance Claims & Prevalence
The Institute of Medicine says that the US healthcare system wastes $75 billion a year on fraud.
- Fraud accounts for 5% to 10% of all claim costs for US and Canadian insurers.
- 32% of insurers say fraud is as high as 20% of claim costs.
- 57% of insurers predict an increase in personal property fraud policyholders.
- 61% of insurers predict an increase in auto insurance fraud by organized rings.
- 69% of insurers predict a rise in workers compensation scams.
Public Attitudes to Insurance Fraud
- More than 1 in 2 people think it is more likely that an insurer’s poor service will cause a person to commit insurance fraud.
- More than 3 in 4 people think that people are more likely to commit insurance fraud during a recession.
- More than 4 in 5 people think it is unethical to misrepresent facts on an insurance application in order to lower their premiums.
- Only 1 in 5 people who say they know about a fraud report the crime.
Types of Insurance Fraud
Automotive
- 21% of bodily-injury claims & 18% of personal injury protection claims that close with payment have the appearance of fraud or build-up.
- Build-up involves inflating otherwise legitimate claims.
- This is the most common abuse.
Arson
- Insurance fraud is suspected in 8% of intentional fires.
- The bedroom is the most common area of origin for intentional home fires.
- Arson is now in decline, but it caused $1.3 billion in direct property damages in the US annually between 2007 & 2011.
Workers Compensation
- More than 1 in 10 small business owners are concerned an employee will fake an injury or illness to get workers compensation benefits.
- 1 in 5 feel unsure about how to identify workers compensation scams.
- It is not just employees contributing to fraud. 10% – 20% of businesses misclassify at least 1 worker as an ‘independent contractor’ to avoid paying full workers compensation premiums.
Medical Identity Theft
- Medical identity theft is when personal information is stolen aby criminals who lodge fraudulent claims against the victim’s health insurance policy.
- Incidents increased by almost 22% in 2014 & it takes 3 months on average for a victim to find out that it has happened to them.
- More than 3 in 5 victims pay an average of $13,500 to resolve the crime.
Anti-Fraud Technology in the Insurance Industry
- 1 in 3 insurers do not feel adequately protected against fraud.
- Yet 95% of insurers do use fraud technology, which is up by 7% compared to the year 2012.
- Just 4 out of 5 insurers (81%) use basic anti-fraud tools.
- These include automated red flags & business rules.
- Advanced anti-fraud tools are not as prevalent among insurers.
- These include link analysis (50%), predictive modeling and text mining (both at 43%).
- Over ½ of insurers (53%) cite a lack of IT resources as the main barrier for implementing advanced anti-fraud technology.
Key Takeaways
- The insurance industry attracts a high rate of fraud & certain lines of insurance are more susceptible than others.
- Insurers need to upgrade their basic anti-fraud tools, identify any IT resources needed as a result & implement advanced software.
- The public needs to be more vigilant in reporting insurance fraud if they become aware of it.